Shin Splints vs Stress Fracture: The Comparison Guide
Shin splints vs stress fracture discussion is different, even though they may bring about similar shin pain, are two different kinds of injuries. Shin splints occur when there is inflammation in the muscles, tendons and other connective tissues around your shinbone but stress fractures are tiny cracks that form inside the bone itself. These types of injuries happen due to overuse and are usually seen in runners.
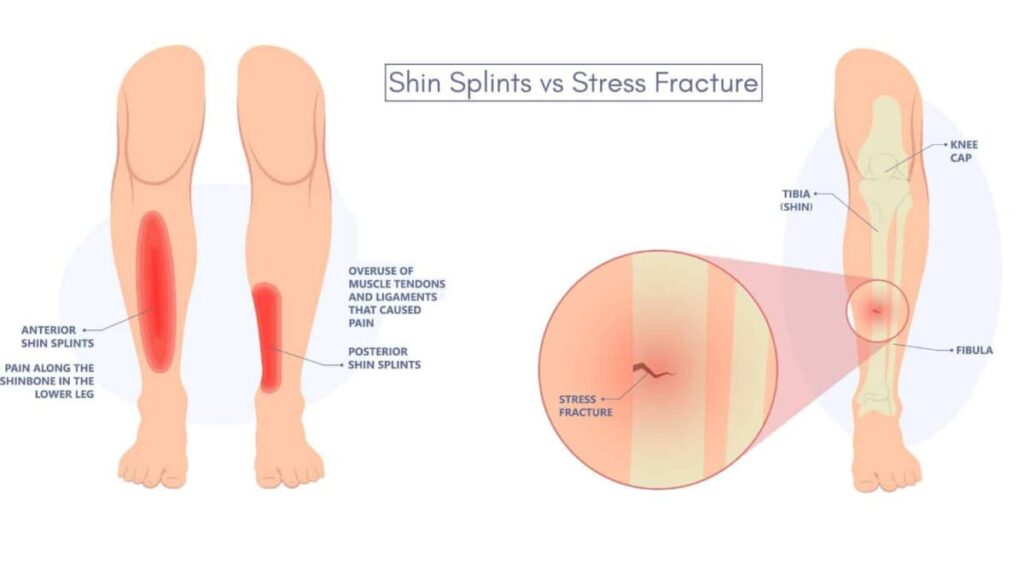
The main dissimilarities of shin splints versus stress fracture are found in the pain pattern. Shin splints usually give rise to a dull ache that spreads out over a wider area, whereas stress fractures cause sharp hurting at one particular point.
Understanding Shin Splints
Shin splints are a usual type of injury related to using the lower leg too much, especially seen in runners and sports people. They happen when muscles, tendons and connective tissues that surround the shinbone become tired from being used too often and get swollen. This inflammation comes up because of repeated pressure on these tissues due to:
– Your shin muscles and connective tissues may be overloaded when you push yourself excessively, especially if you just began a new exercise routine.
– Shoes that do not provide enough support or cushioning can cause incorrect positioning of the feet and strain on shins when doing activities.
– Feet that are flat or have very high and stiff arches can change how your foot hits the ground, causing more pressure on the shin muscles and tissues.
A Look At Stress Fracture
When studying shin splints vs stress fracture, one should know that stress fractures are tiny breaks that form inside a bone, usually the shinbone, from repeated stress. Like shin splints, they are often linked to activities of excessive use such as running and jumping.
– If you increase the strength or length of your exercise routine too quickly, it can surpass the bone’s capacity to adjust and result in tiny fractures.
– For instance, osteoporosis is a condition that causes bones to become fragile and weak. Even normal actions might result in stress fractures due to this ailment.
– When a person has either flat feet or arches that are too stiff, it changes the forces on their shinbone and can lead to more chances of getting stress fractures.
Not eating enough calcium and vitamin D can lead to problems with bone health, which might result in stress fractures.
Key Differences: shin splints vs stress fracture
| Features | Shin Splints | Stress Fractures |
| Affected Tissue | The connective ligaments, muscles, and tendons around the shinbone | Shinbone itself |
| Cause | Abuse, inappropriate footwear, and an abrupt rise in training | Overtraining, low bone density, and abrupt increase in training |
| Pain Pattern | Dull pain that spreads throughout the shinbone, frequently in the lower third | Sharp discomfort in a particular area of the shinbone |
| Pain Onset | Warming up may help with some pain relief. | Any weight-bearing action, such as walking, makes the pain worse. |
| Swelling | Minimal | Feel soreness and edema at the fracture site |
| Diagnosis | physical examination and occasionally imaging studies | An MRI, an X-ray, a physical examination, or a bone scan |
| Treatment | Take NSAIDs, rest, ice, compression, elevation, and gradually resume your activities. | Rest, immobilization, physical therapy, extended recovery time |
When to Seek Professional Help
Though shin splints vs stress fractures have similar symptoms, it is very important to get a definite diagnosis so that the proper treatment can be decided. A doctor or physical therapist may do a complete physical check-up and possibly use imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs to distinguish between these two conditions.
Not paying attention to persistent shin pain can cause more serious problems. If you leave shin splints without treatment, they might get worse and turn into stress fractures or long-lasting pain.
The same way, if there is a small crack in your bone due to stress fracture but you delay treating it, the crack might grow bigger which will make healing take longer and raise chances of complications.
Prevention is Key
When it comes to shin splints vs stress fractures, there are a number of actions that can be taken to lower the chances of having these painful problems:
Don’t make sudden jumps in running distance, intensity or frequency. Increase your mileage and workout strength slowly to give time for your muscles, tendons and bones to adjust with the growing pressure.
Keep a proper running style during all your runs. This means paying attention to the right body position, how your feet touch the ground and the length of each step to lower strain on your shins and lower legs.
Include exercises for the muscles around your shins, calves and ankles. Strong muscles give more support and shock absorption, lessening the load on your bones and connective tissues.
Select running shoes with good cushioning and support for your type of foot. Make sure to change your running shoes when they get old, which is usually after 300-500 miles. This is important because wearing out of shoes can affect the support they give and increase the possibility of injury.
Put activities such as swimming, cycling or yoga into your routine. These let your legs rest from the running’s repeated strain while still keeping up fitness levels overall.
Eat a wide-ranging diet that includes calcium and vitamin D, both necessary to keep bones strong and prevent stress fractures.
Shin splints vs stress fractures, both causing pain in the shin area frequently, are two types of running injuries that share common symptoms.




